Introduction
As enterprises scale across regions, platforms, and data sources, governance becomes one of the most critical and most misunderstood pillars of analytics success. Many organizations invest heavily in cloud platforms, AI models, and dashboards, yet still struggle with unreliable reports, compliance exposure, and low trust in data. The root cause is often the absence of a well-defined data governance framework.
A centralized data governance framework provides the structure that allows data to be trusted, reused, and scaled safely. It creates clarity around ownership, accountability, quality, and access while enabling analytics and AI initiatives to operate with confidence. For global enterprises, governance is no longer optional. It is foundational to performance, risk management, and long-term strategy.
What Is a Centralized Data Governance Framework
A centralized data governance framework is an enterprise-wide system of policies, roles, processes, and controls that manage how data is created, accessed, secured, and used. Governance decisions are coordinated through a central authority or operating model rather than being fragmented across departments.
This approach does not remove flexibility from teams. Instead, it establishes shared standards and guardrails that ensure consistency while allowing business units to operate efficiently. A strong data governance framework aligns business objectives, regulatory requirements, and technical execution into a single, trusted model.
Why Data Governance Is a Top Enterprise Priority
Governance has moved into the spotlight as data environments become more complex and more regulated. Enterprises are now accountable not only for how data is used, but also for how decisions are made using that data.
Key drivers pushing governance to the forefront include:
- Increasing regulatory scrutiny across industries and regions
- Rapid adoption of AI and advanced analytics
- Multi-cloud and hybrid data architectures
- Rising cost of poor data quality and rework
- Executive and board-level accountability for data-driven decisions
Without a centralized data governance framework, organizations often experience duplicated metrics, conflicting reports, slow audits, and declining confidence in analytics outputs.
Core Components of a Centralized Data Governance Framework
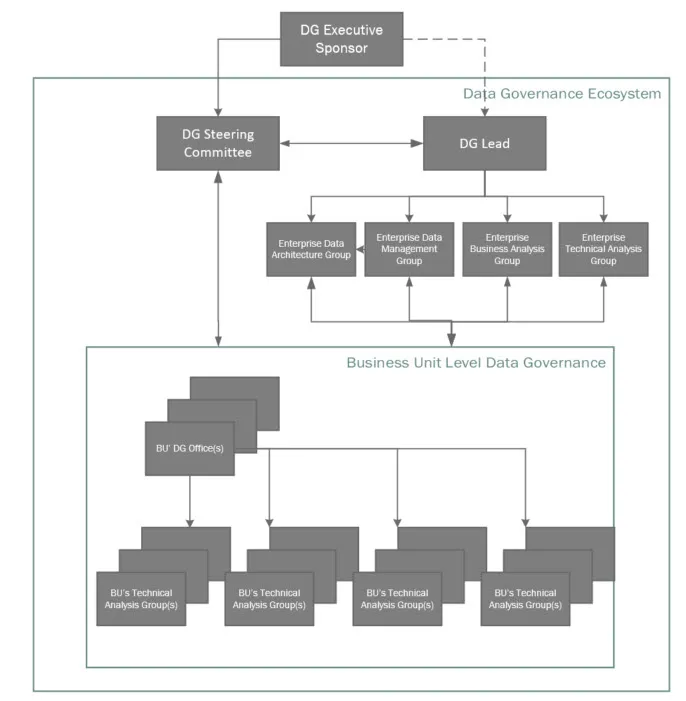

A governance framework succeeds when its components work together as an integrated system.
Data Ownership and Stewardship
Clear ownership is the backbone of governance. Each critical dataset should have a defined data owner responsible for accuracy, usage, and compliance. Data stewards support owners by managing quality rules, definitions, and issue resolution.
This structure eliminates ambiguity and ensures accountability when data issues arise.
Policies and Standards
Policies define how data is classified, stored, shared, and retained. Standards ensure consistent naming conventions, definitions, and formats across systems. Together, they prevent confusion and make analytics outputs comparable across teams and regions.
Data Quality Management
Quality controls ensure data remains accurate, complete, and timely. Validation rules, monitoring, and remediation workflows are essential for analytics, reporting, and AI initiatives. Many enterprises strengthen this capability through dedicated data quality and validation solutions available at https://dataguruanalytics.org/data-quality-validation-solutions.
Security and Access Control
Governance frameworks define who can access which data and under what conditions. Role-based access, encryption, and audit logging protect sensitive information while enabling legitimate business use.
Metadata and Lineage
Metadata management provides visibility into what data exists, where it comes from, and how it is used. Lineage tracking supports impact analysis, regulatory audits, and trust in analytics results.
How to Build a Centralized Data Governance Framework
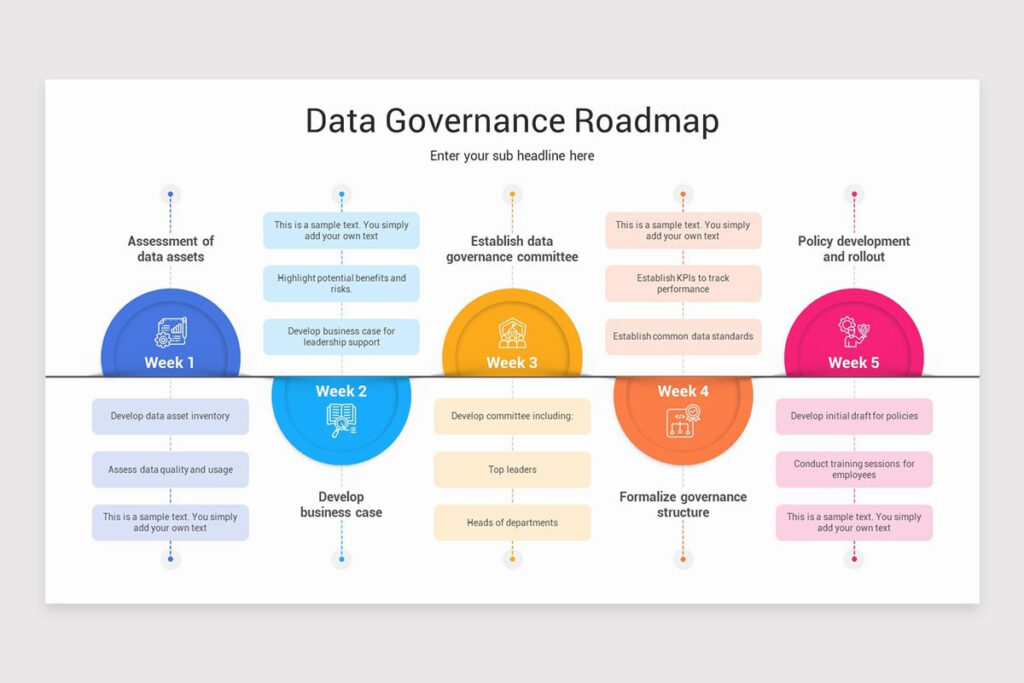
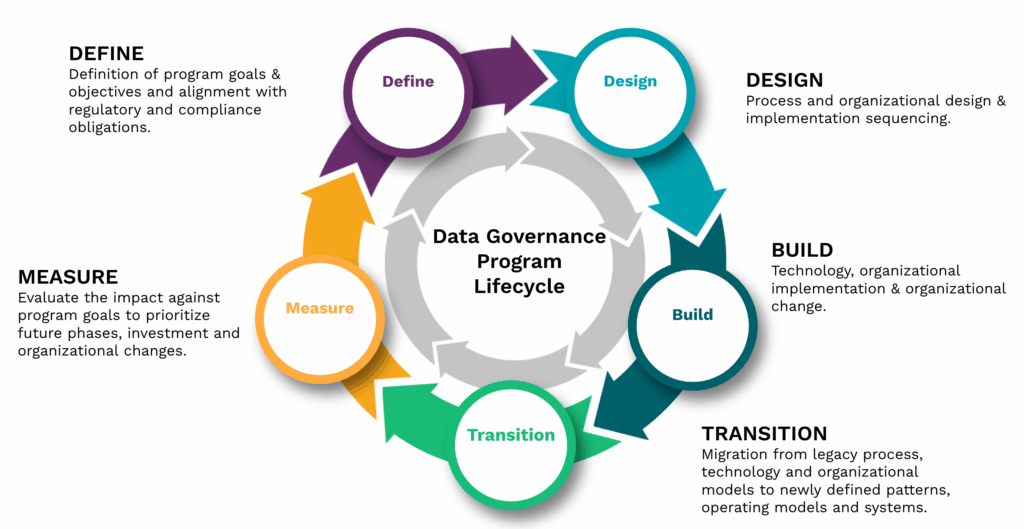
Step 1 Secure Executive Sponsorship
Governance initiatives require strong leadership support. Executives must position data governance as a strategic priority rather than a technical exercise. Sponsorship ensures alignment, funding, and enforcement across the organization.
Step 2 Define Scope and Objectives
Not all data carries the same level of risk or value. Start by identifying critical domains such as finance, customer data, operations, or compliance reporting. Define governance objectives that align with business outcomes.
Step 3 Design the Governance Operating Model
Establish how governance decisions are made and who participates. This often includes a governance council, data owners, data stewards, and technical enablement teams. Clear escalation paths prevent delays and conflicts.
Step 4 Enable Governance with Technology
Technology makes governance scalable. Data catalogs, quality monitoring tools, access management platforms, and lineage solutions help enforce policies and provide transparency. Cloud-native platforms allow centralized governance even in distributed environments.
Step 5 Embed Governance into Daily Operations
Governance should not feel like an extra layer of bureaucracy. Quality checks, access approvals, and policy enforcement should be integrated into existing workflows so governance becomes part of normal operations.
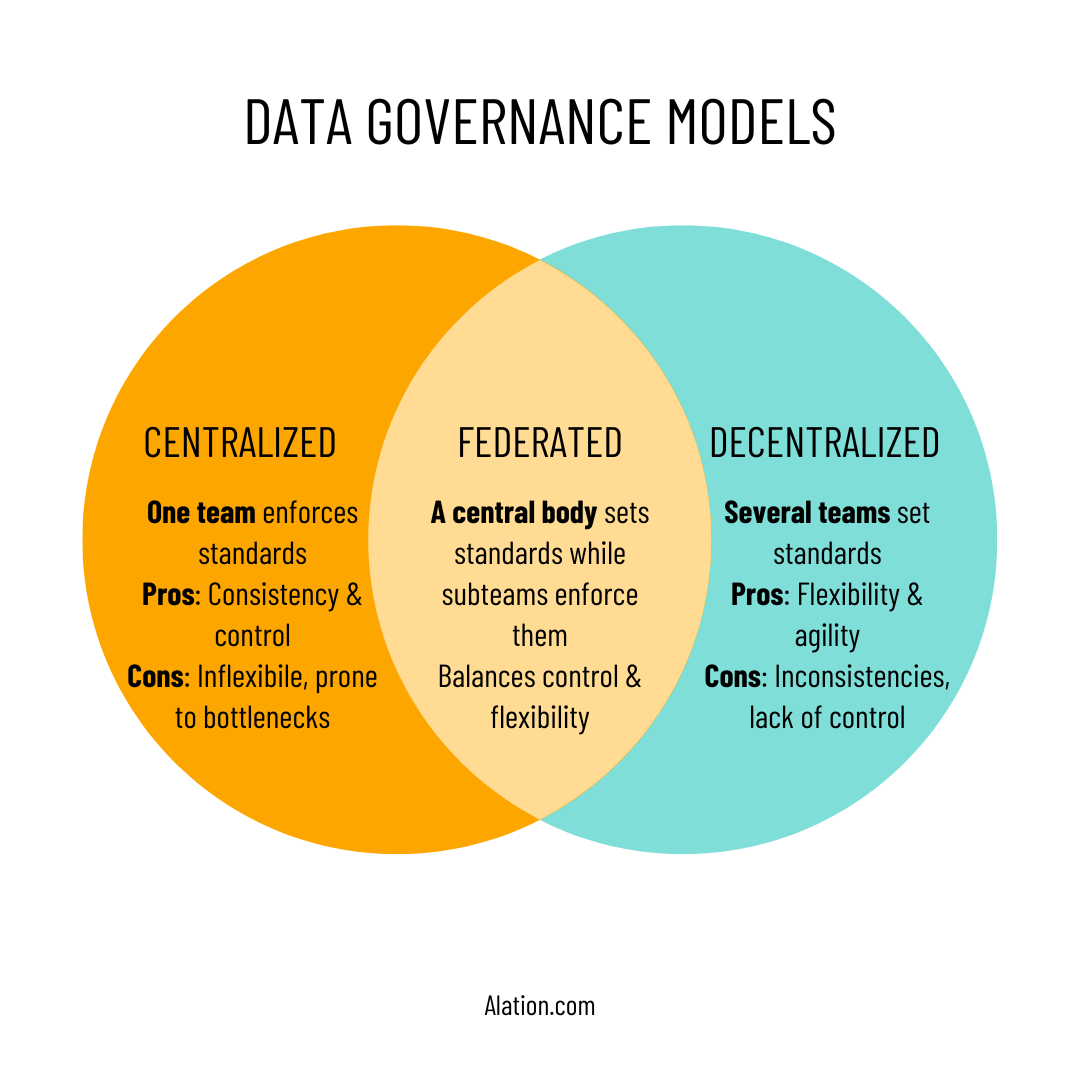
Centralized Governance Versus Decentralized Models
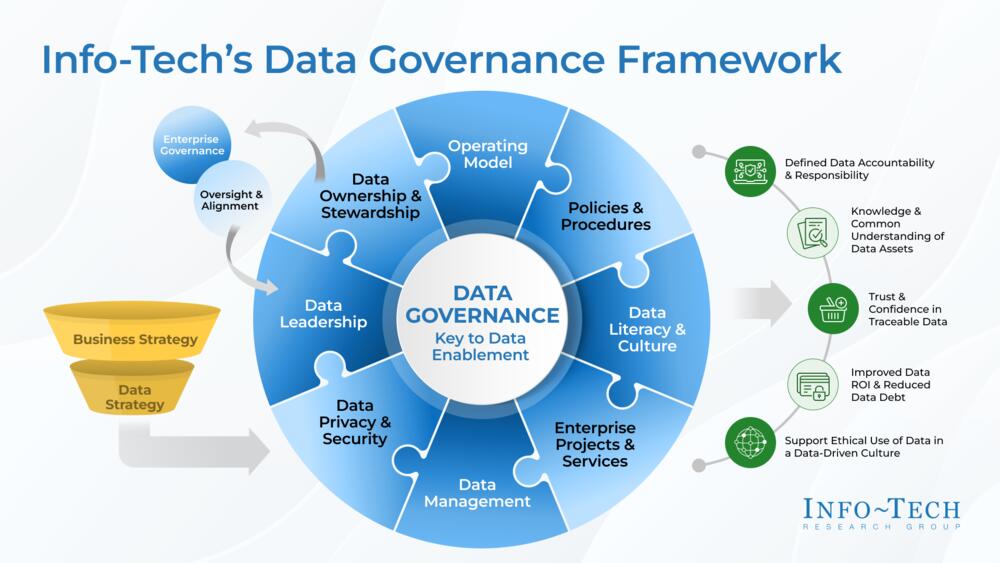
Decentralized governance models often emerge organically but tend to create silos, inconsistent metrics, and duplicated effort. Centralized data governance provides consistency, scalability, and stronger risk management.
Modern enterprises often adopt a hybrid approach where standards and oversight are centralized, while execution remains flexible within defined boundaries. This balance enables speed without sacrificing trust.
Common Governance Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Governance initiatives often face resistance due to perceptions of control or added workload. Common challenges include unclear ownership, low data literacy, and lack of measurable outcomes.
Successful organizations address these challenges by:
- Communicating governance benefits in business terms
- Focusing on enablement rather than restriction
- Providing training and clear documentation
- Starting with high-impact data domains
- Demonstrating early wins through improved analytics outcomes
When positioned correctly, governance becomes a value enabler rather than a constraint.
The Role of Data Governance in Analytics and AI
Analytics and AI systems depend on trusted data. A centralized data governance framework ensures models are trained on consistent, compliant, and well-understood datasets.
As enterprises deploy AI at scale, governance becomes even more critical. Explainability, bias mitigation, and auditability all rely on strong data controls. Organizations building AI-ready data environments often begin with governance-led architecture design supported by strategic advisory services such as those offered at https://dataguruanalytics.org/services/research-consultancy/.
Measuring the Success of a Data Governance Framework
Governance effectiveness should be measured using both technical and business indicators.
Key metrics include:
- Reduction in data quality issues
- Faster audit and compliance cycles
- Improved consistency across reports and dashboards
- Increased reuse of governed data assets
- Higher confidence in analytics and AI outputs
These indicators demonstrate whether governance is strengthening decision-making and reducing enterprise risk.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a centralized data governance framework suitable for global enterprises
Yes. Centralized governance provides consistent standards while supporting regional compliance and operational needs when designed thoughtfully.
Will centralized governance slow down analytics teams
When implemented correctly, it reduces rework and accelerates analytics by eliminating confusion and data disputes.
How long does it take to implement a data governance framework
Initial frameworks can be established within six to twelve months, followed by continuous improvement as the organization matures.
Conclusion
A centralized data governance framework is the foundation of trustworthy analytics, regulatory confidence, and scalable AI initiatives. Enterprises that invest in governance early reduce risk, improve data confidence, and unlock faster, more reliable decision-making. In a data-driven economy, governance is not a constraint. It is a strategic advantage.
Call to Action:
Build data systems your leaders can trust. Explore expert guidance on designing and implementing a centralized data governance framework at https://dataguruanalytics.org and strengthen the foundation of your enterprise analytics strategy.