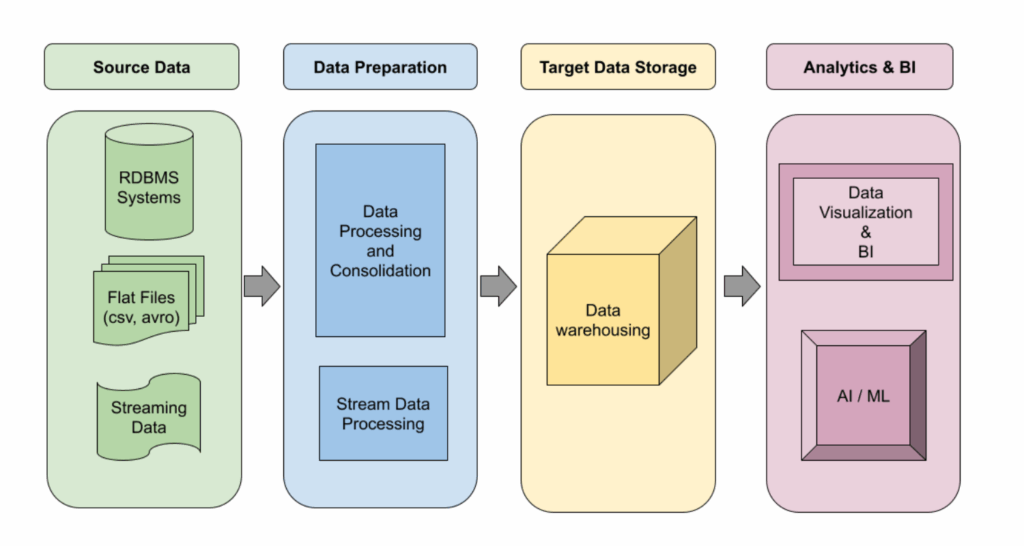
Introduction
As enterprises expand across regions, markets, and digital channels, data pipelines become the backbone of global operations. Customer interactions, transactions, sensors, and applications generate continuous streams of data that must be processed reliably and delivered on time. When pipelines fail to scale, analytics slow down, decisions rely on outdated information, and operational risk increases.
Designing scalable data pipelines is no longer a purely engineering concern. It is a strategic requirement for organizations operating across multiple geographies, time zones, and cloud environments. Enterprises that invest in scalable pipeline architecture gain speed, resilience, and the ability to adapt as data volumes and business demands grow.
What Are Scalable Data Pipelines
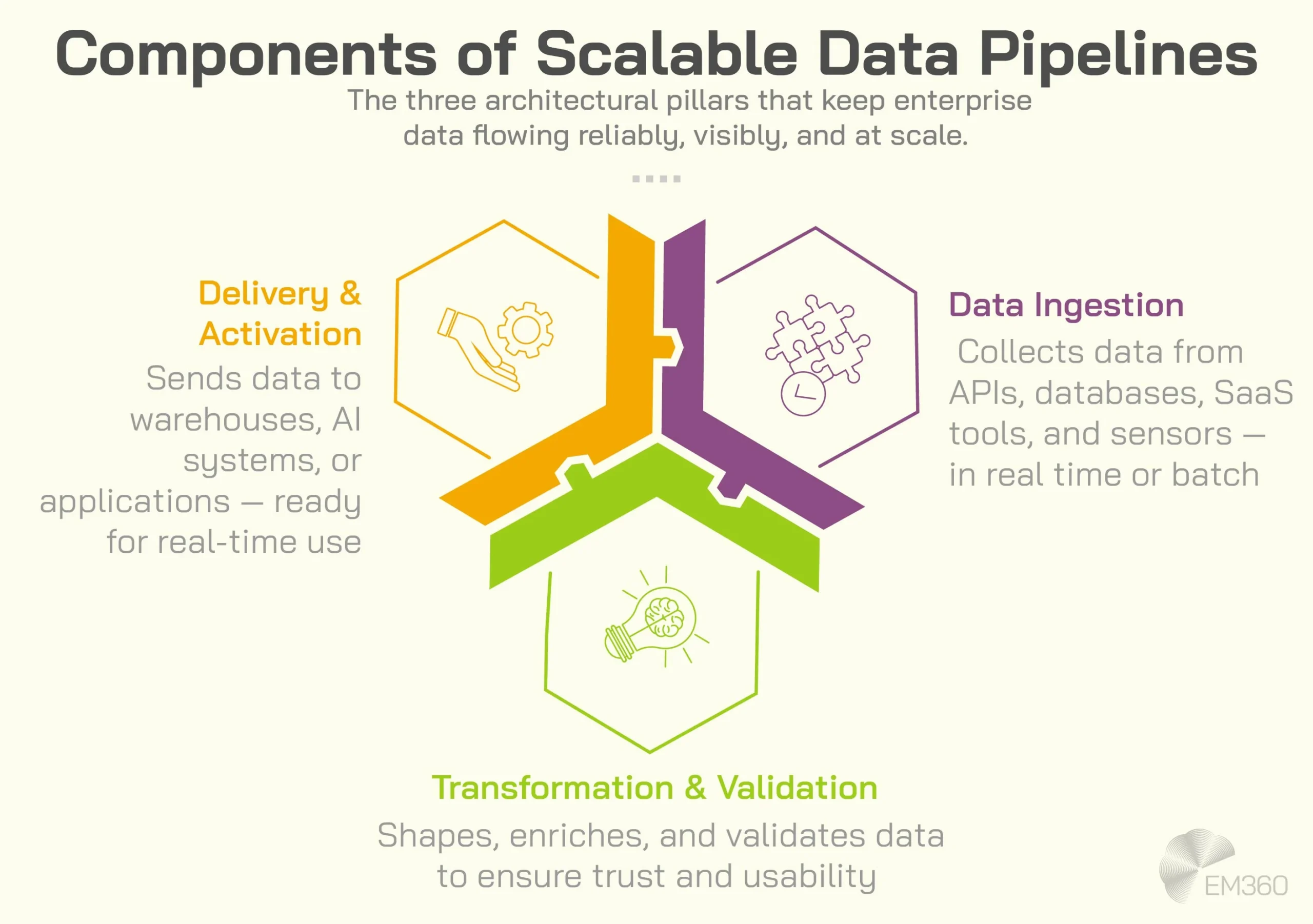
Scalable data pipelines are systems designed to ingest, process, and deliver data reliably as volume, velocity, and complexity increase. They maintain performance and accuracy even as new sources, users, and regions are added.
Unlike traditional batch pipelines built for limited scope, modern scalable data pipelines support real time and near real time processing. They are designed to handle unpredictable workloads while ensuring data quality, security, and availability across global operations.
Why Global Operations Demand Scalable Pipelines
Global enterprises face challenges that local systems were never designed to handle. Data arrives continuously from multiple regions, often with different formats, latency requirements, and regulatory constraints.
Key pressures driving the need for scalable data pipelines include:
- Rapid growth in data volume and sources
- Real time analytics requirements for decision making
- Multi region and multi cloud architectures
- Around the clock operations across time zones
- Increased reliance on AI and automation
Without scalable pipelines, organizations experience delays, inconsistencies, and growing operational friction.
Core Principles of Scalable Data Pipeline Design
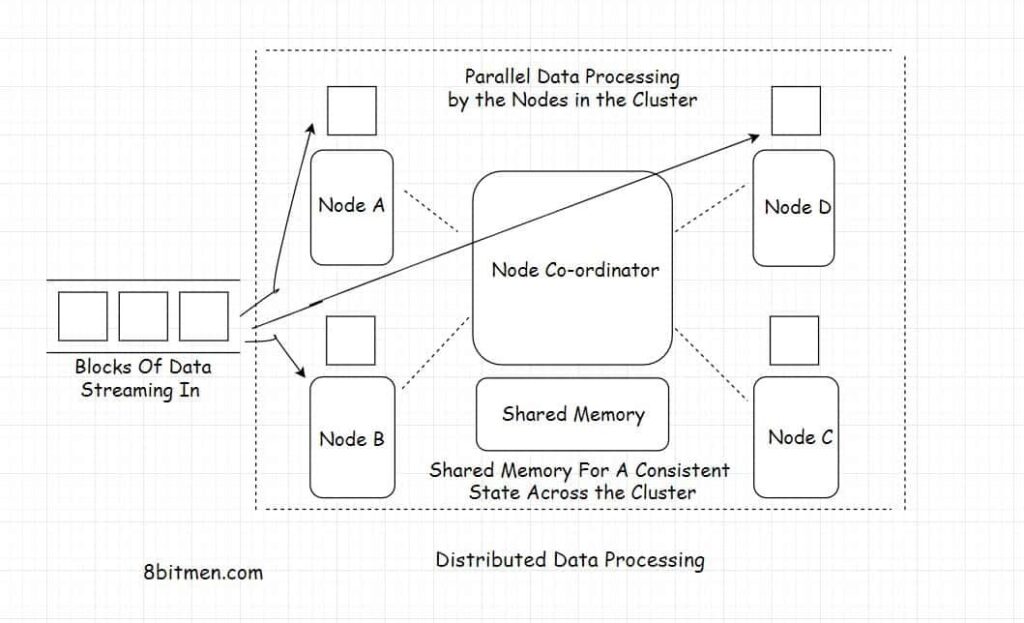
Successful pipeline design follows a set of core engineering principles that ensure long term scalability.
Modularity and Loose Coupling
Pipelines should be built as modular components rather than monolithic systems. Ingestion, processing, storage, and consumption layers should operate independently. This allows teams to scale or update one component without disrupting others.
Horizontal Scalability
Scalable data pipelines grow by adding resources rather than redesigning systems. Distributed processing frameworks and cloud native services allow workloads to scale dynamically as demand changes.
Fault Tolerance and Resilience
Failures are inevitable in global systems. Pipelines must detect failures, recover automatically, and prevent data loss or duplication. Built in retry mechanisms and checkpointing improve reliability.
Consistent Data Quality Controls
Scalability without quality creates unreliable analytics. Validation, schema enforcement, and anomaly detection must scale alongside volume and velocity. Many enterprises strengthen this layer through data quality and validation solutions such as https://dataguruanalytics.org/data-quality-validation-solutions.
Architectures for Global Data Pipelines
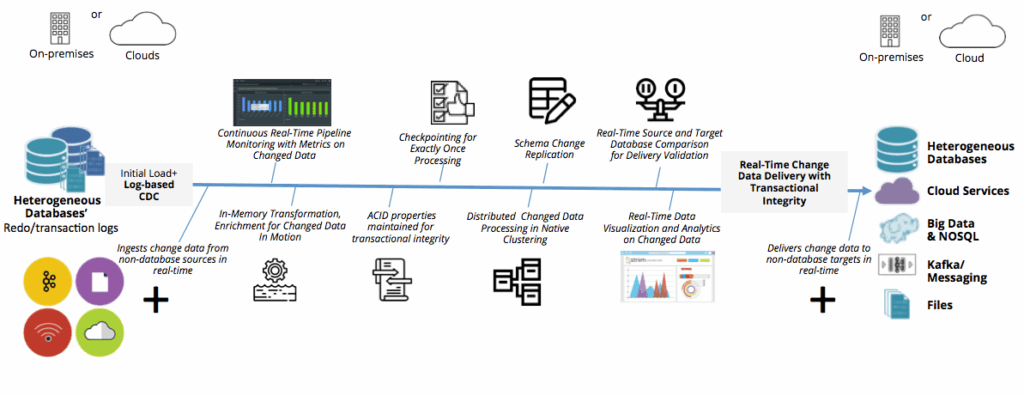
Modern enterprises typically combine multiple architectural patterns to support global needs.
Batch Processing Pipelines
Batch pipelines process large volumes of data at scheduled intervals. They are effective for reporting, historical analysis, and cost optimized workloads. However, they introduce latency that may not suit time sensitive use cases.
Streaming Pipelines
Streaming pipelines process data continuously as it arrives. They support real time dashboards, alerts, and automated decision making. For global operations, streaming reduces latency and improves responsiveness.
Hybrid Architectures
Most enterprises adopt hybrid models that combine batch and streaming pipelines. This approach balances performance, cost, and flexibility across diverse use cases.
Engineering Challenges at Global Scale
Designing scalable data pipelines introduces challenges that increase with scale.
Common issues include:
- Network latency between regions
- Inconsistent data formats across sources
- Cost management for continuous processing
- Monitoring and observability across distributed systems
- Coordinating schema changes without disruption
Addressing these challenges requires disciplined engineering practices and continuous monitoring.
Building Pipelines That Support Analytics and AI
Scalable data pipelines play a critical role in analytics and machine learning. Models depend on timely, consistent data to perform accurately.
Best practices include:
- Ensuring training and production pipelines use consistent logic
- Supporting feature reuse across teams
- Monitoring data drift and pipeline health continuously
- Aligning pipeline design with governance and security standards
Enterprises often align pipeline engineering with broader data architecture strategy through advisory services such as https://dataguruanalytics.org/services/research-consultancy/.
Security and Governance in Scalable Pipelines
As pipelines scale, security and governance become increasingly important. Data must be protected as it moves across regions and systems.
Key considerations include:
- Encryption of data in transit and at rest
- Role based access controls for pipeline components
- Audit logging and lineage tracking
- Compliance with regional data regulations
Integrating security and governance early prevents costly retrofits later.
Measuring the Performance of Scalable Data Pipelines
Enterprises should track metrics that reflect both technical and business performance.
Key indicators include:
- Data latency from source to consumption
- Pipeline uptime and failure rates
- Cost efficiency per data volume processed
- Data quality incident frequency
- Analytics and AI performance stability
These metrics help teams understand whether pipelines are supporting global operations effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do scalable data pipelines differ from traditional ETL systems
Scalable pipelines are designed for continuous growth, real time processing, and distributed environments, while traditional ETL systems focus on periodic batch jobs.
Are scalable pipelines only needed by large enterprises
No. Organizations planning global expansion or advanced analytics benefit from scalable design early to avoid technical debt.
How long does it take to build scalable data pipelines
Initial implementations can be delivered within months, with scalability improving over time as usage grows.
Conclusion
Scalable data pipelines are the foundation of global digital operations. Enterprises that design pipelines for growth, resilience, and quality gain faster insights, stronger analytics, and greater operational confidence. In a world where data never stops moving, scalable pipeline engineering is not optional. It is essential for sustained global performance.
Call to Action:
Design data pipelines built for global scale and reliability. Explore expert guidance on scalable data pipeline engineering at https://dataguruanalytics.org and strengthen the backbone of your enterprise analytics ecosystem.